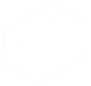
Bangladesh Judiciary Court Structure (Part-1)
The court structure in Bangladesh
Figure: The court structure in Bangladesh
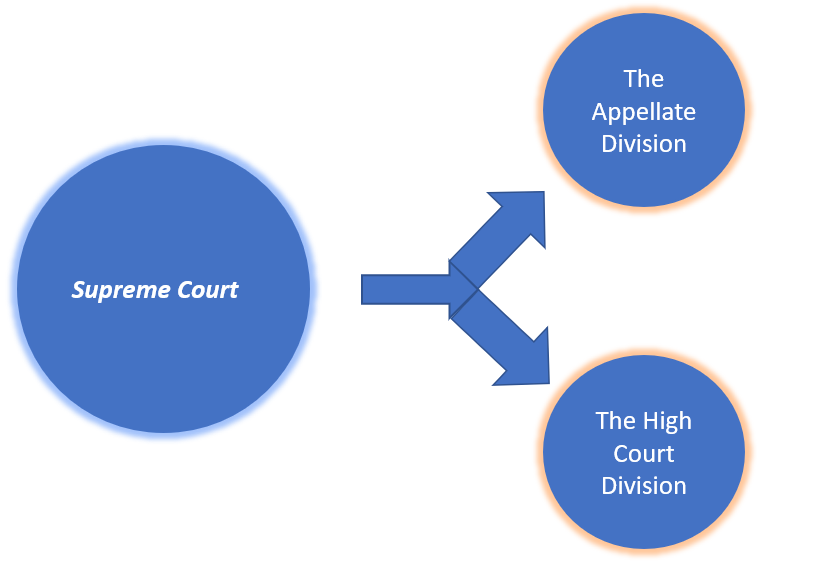
Supreme Court
The apex court of the country consisting of two divisions i.e. the Appellate Division and the High Court Division. Chief Justice of Bangladesh and other judges in each division constitute the Supreme Court. Chief justice and other judges are independent in the exercise of their judicial functions subject to the provisions of the Constitution. The Chief Justice and other judges are appointed by the President in accordance with the advice of the Prime Minister. Judges of the Supreme Court are appointed from amongst the advocates of the Supreme Court and judicial officers. Judges appointed in the Appellate Division sit in that division with the Chief Justice, and the judges appointed in the High Court Division sit in that division.
Figure : Supreme courts 2 division
The high court division has the power of judicial review. On the application of any aggrieved person, the high court division may give such directions or orders to any person or authority including a person performing any function in connection with the affairs of the Republic for the enforcement of any of the fundamental rights guaranteed under the Constitution. In enforcing the fundamental rights, the high court division is empowered to declare any law inconsistent with the fundamental right or any other part of the Constitution void to the extent of the inconsistency. High court division has also original jurisdiction in cases relating to the company, admiralty, matrimonial issues, trademarks, copyrights, etc. The high court division may also withdraw a case from any subordinate court and dispose of the same if any substantial question of law as to the interpretation of the Constitution or a point of general public importance is involved in that case.
The high court division has appellate and revisional jurisdictions conferred on it by the laws. An appeal lies to the appellate division as of right from judgment, decree, order, or sentence passed by the high court division where the high court division certifies that the case involves a substantial question of law as to the interpretation of the Constitution of Bangladesh or has sentenced a person to death or imprisonment for life or has imposed punishment for contempt of that court.
Subordinate civil judiciary
There are five classes of subordinate civil courts i.e. the courts of assistant judges, senior assistant judges, joint district judges, additional district judges, and district judges. The district judge is the head of the judiciary in each of the districts. In the hill districts where there were no separate civil courts, the magistrates performed the functions of the civil courts. But recently civil courts have been sitting there and functioning. Subject to the superintendence of the high court division, the district judge has administrative control over all the civil courts of the district. District judge has mainly appellate as well as revisional jurisdiction, but in some matters, he has original jurisdiction too. The jurisdiction of the additional judge is co-extensive with that of the district judge. He/she discharges the judicial business assigned to him/her by the district judge. Appeals to the judgments, decrees, and orders passed by the assistant judges and subordinate judges lie to the district judge. Similarly, a district judges may transfer the appeals preferred against judgments, decree, or orders passed by the assistant judges to the joint district judges for disposal. Joint district judges have unlimited civil original jurisdiction.
Figure: Subordinate civil judiciary class
Civil courts while deciding any question regarding succession, inheritance, marriage or caste or any religious usage or institution apply the Muslim law in cases where the parties are Muslims and' Hindu law in cases where the parties are Hindus except so far as such law has been altered or abolished by any enactment made by the legislature.
Artha Rin Adalat (Loan Court) has been set up in each district under the provisions of the Artha Rin Adalat Ain 1990 by the government appointing subordinate judges as judges of such courts in consultation with the supreme court. All suits for realization of the loan of the financial institutions eg bank, investment corporation, house building finance corporation, leasing company, etc and non-banking financial institutions constituted under the provisions of Financial Institutions Act 1993, are to be filed in the Artha Rin Adalats, and such suits are exclusively triable by such courts. Artha Rin Adalat is a civil court and has all the powers of the civil court.
Delia Adalat (Bankruptcy Court) has been constituted under the Bankruptcy Act, 1997. District court in each district is the Bankruptcy court of that district, and district judge is the presiding judge of that court and is authorized to deal with and dispose of bankruptcy cases arising within the district and he/she may authorize an additional (district) judge to deal with and dispose of any such case.
Assistant judges, senior assistant judges as well as joint district judges have been empowered with the functions of Courts of Small Cause to entertain and try suits for the realization of money up to thirty thousand takas and for ejectment of the monthly tenant by the landlord when twelve months' rent of the premises is equivalent to the above amount. No appeal lies from the decree or most of the orders passed by the Court of Small Cause except appeal to the district judge from certain orders. But a revision may be filed to the High Court Division by an aggrieved party against the decree or non-appealable order. Assistant judges and senior assistant judges also perform the functions of the Rent Controller deciding disputes between the landlords and monthly tenants of house premises other than suits for the realization of arrear of rent or ejectment from the rented premises such as deposit of rent by the tenant on the refusal of the landlord to accept the same, repair of the premises, fixation of standard rent, etc. Assistant judges and senior assistant judges also constitute Family Courts to entertain and try suits arising from family disputes such as restitution of conjugal rights, dissolution of marriage, maintenance of wife and children, custody of children, etc.

No Comments